In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly seeking innovative ways to enhance employee experience and productivity. There are many challenges that can impact employee productivity, such as cumbersome search experiences or finding specific information across an organization’s vast knowledge bases. Additionally, with the rise of remote and hybrid work models, traditional support systems such as IT Helpdesks and HR might struggle to keep up with the increased demand for assistance. Productivity loss because of these challenges can lead to lengthy onboarding times for new employees, extended task completion times, and call volumes for undifferentiated IT and HR support, to name a few.
Amazon Q Business is a fully managed, generative artificial intelligence (AI) powered assistant that can address the challenges mentioned above by providing 24/7 support tailored to individual needs. It can handle a wide range of tasks such as answering questions, providing summaries, and generating content and completing tasks based on data in your organization. Additionally, Amazon Q Business offers enterprise-grade data security and privacy and has guardrails built-in that are configurable by an admin. Customers like Deriv were successfully able to reduce new employee onboarding time by up to 45% and overall recruiting efforts by as much as 50% by making generative AI available to all of their employees in a safe way.
In this blog post, we will talk about Amazon Q Business use cases, walk-through an example application, and discuss approaches for measuring productivity gains.
Use cases overview
Some key use cases for Amazon Q Business for organizations include:
- Providing grounded responses to employees: An organization can deploy Amazon Q Business on their internal data, documents, products, and services. This allows Amazon Q Business to understand the business context and provide tailored assistance to employees on common questions, tasks, and issues.
- Improving employee experience: By deploying Amazon Q Business across various environments like websites, apps, and chatbots, organizations can provide unified, engaging and personalized experiences. Employees will have a consistent experience wherever they choose to interact with the generative AI assistant.
- Knowledge management: Amazon Q Business helps organizations use their institutional knowledge more effectively. It can be integrated with internal knowledge bases, manuals, best practices, and more, to provide a centralized source of information to employees.
- Project management and issue tracking: With Amazon Q Business plugins, users can use natural language to open tickets without leaving the chat interface. Previously resolved tickets can also be used to help reduce overall ticket volumes and get employees the information they need faster to resolve an issue.
Amazon Q Business features
The Amazon Q Business-powered chatbot aims to provide comprehensive support to users with a multifaceted approach. It offers multiple data source connectors that can connect to your data sources and help you create your generative AI solution with minimal configuration. Amazon Q Business supports over 40 connectors at the time of writing. Additionally, Amazon Q Business also supports plugins to enable users to take action from within the conversation. There are four native plugins offered, and a custom plugin option to integrate with any third-party application.
Using the Business User Store feature, users see chat responses generated only from the documents that they have access to within an Amazon Q Business application. You can also customize your application environment to your organizational needs by using application environment guardrails or chat controls such as global controls and topic-level controls that you can configure to manage the user chat experience.
Features like document enrichment and relevance tuning together play a key role in further customizing and enhancing your applications. The document enrichment feature helps you control both what documents and document attributes are ingested into your index and also how they’re ingested. Using document enrichment, you can create, modify, or delete document attributes and document content when you ingest them into your Amazon Q Business index. You can then assign weights to document attributes after mapping them to index fields using the relevance tuning feature. You can use these assigned weights to fine-tune the underlying ranking of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)-retrieved passages within your application environment to optimize the relevance of chat responses.
Amazon Q Business offers robust security features to protect customer data and promote responsible use of the AI assistant. It uses pre-trained machine learning models and does not use customer data to train or improve the models. The service supports encryption at rest and in transit, and administrators can configure various security controls such as restricting responses to enterprise content only, specifying blocked words or phrases, and defining special topics with customized guardrails. Additionally, Amazon Q Business uses the security capabilities of Amazon Bedrock, the underlying AWS service, to enforce safety, security, and responsible use of AI.
Sample application architecture
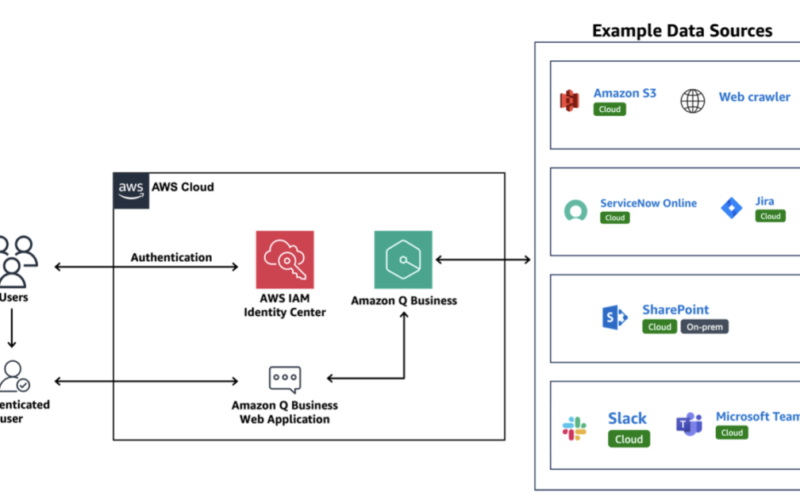
The following figure shows a sample application architecture.
Application architecture walkthrough
Before you begin to create an Amazon Q Business application environment, make sure that you complete the setting up tasks and review the Before you begin section. This includes tasks like setting up required AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and enabling and pre-configuring an AWS IAM Identity Center instance.
As the next step towards creating a generative AI assistant, you can create the Amazon Q Business web experience. The web experience can be created using either the AWS Management Console or the Amazon Q Business APIs.
After creating your Amazon Q Business application environment, you create and select the retriever and provision the index that will power your generative AI web experience. The retriever pulls data from the index in real time during a conversation. After you select a retriever for your Amazon Q Business application environment, you connect data sources to it.
This sample application connects to repositories like Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and SharePoint, and to public facing websites or internal company websites using Amazon Q Web Crawler. The application also integrates with service and project management tools such as ServiceNow and Jira and enterprise communication tools such as Slack and Microsoft Teams. The application uses built-in plugins for Jira and ServiceNow to enable users to perform specific tasks related to supported third-party services from within their web experience chat, such as creating a Jira ticket or opening an incident in ServiceNow.
After the data sources are configured, data is integrated and synchronized into container indexes that are maintained by the Amazon Q Business service. Authorized users interact with the application environment through the web experience URL after successfully authenticating. You could also use Amazon Q Business APIs to build a custom UI to implement special features such as handling feedback, using company brand colors and templates, and using a custom sign-in. It also enables conversing with Amazon Q through an interface personalized to your use case.
Application demo
Here are a few screenshots demonstrating an AI assistant application using Amazon Q Business. These screenshots illustrate a scenario where an employee interacts with the Amazon Q Business chatbot to get summaries, address common queries related to IT support, and open tickets or incidents using IT service management (ITSM) tools such as ServiceNow.
- Employee A interacts with the application to get help when wireless access was down and receives suggested actions to take:

- Employee B interacts with the application to report an incident of wireless access down and receives a form to fill out to create a ticket:


An incident is created in ServiceNow based on Employee B’s interaction:
- A new employee in the organization interacts with the application to ask several questions about company policies and receives reliable answers:

- A new employee in the organization asks the application how to reach IT support and receives detailed IT support contact information:

Approaches for measuring productivity gains:
There are several approaches to measure productivity gains achieved by using a generative AI assistant. Here are some common metrics and methods:
Average search time reduction: Measure the time employees spend searching for information or solutions before and after implementing the AI assistant. A reduction in average search time indicates faster access to information, which can lead to shorter task completion times and improved efficiency.
-
- Units: Percentage reduction in search time or absolute time saved (for example, hours or minutes)
- Example: 40% reduction in average search time or 1 hour saved per employee per day
Task completion time: Measure the time taken to complete specific tasks or processes with and without the AI assistant. Shorter completion times suggest productivity gains.
-
- Units: Percentage reduction in task completion time or absolute time saved (for example, hours or minutes)
- Example: 30% reduction in task completion time or 2 hours saved per task
Recurring issues: Monitor the number of tickets raised for recurring issues and issues related to tasks or processes that the AI assistant can handle. A decrease in these tickets indicates improved productivity and reduced workload for employees.
-
- Units: Percentage reduction in recurring issue frequency or absolute reduction in occurrences
- Example: 40% reduction in the frequency of recurring issue X or 50 fewer occurrences per quarter
Overall ticket volume: Track the total number of tickets or issues raised related to tasks or processes that the AI assistant can handle.
-
- Units: Percentage reduction in ticket volume or absolute number of tickets reduced
- Example: 30% reduction in relevant ticket volume or 200 fewer tickets per month
Employee onboarding duration: Evaluate the time required for new employees to become fully productive with and without the AI assistant. Shorter onboarding times can indicate that the AI assistant is providing effective support, which translates to cost savings and faster time-to-productivity.
-
- Units: Percentage reduction in onboarding time or absolute time saved (for example, days or weeks)
- Example: 20% reduction in onboarding duration or 2 weeks saved per new employee
Employee productivity metrics: Track metrics such as output per employee or output quality before and after implementing the AI assistant. Improvements in these metrics can indicate productivity gains.
-
- Units: Percentage improvement in output quality or reduction in rework or corrections
- Example: 15% improvement in output quality or 30% reduction in rework required
Cost savings: Calculate the cost savings achieved through reduced labor hours, improved efficiency, and faster turnaround times enabled by the AI assistant.
-
- Units: Monetary value (for example, dollars or euros) saved
- Example: $100,000 in cost savings due to increased productivity
Knowledge base utilization: Measure the increase in utilization or effectiveness of knowledge bases or self-service resources because of the AI assistant’s ability to surface relevant information.
-
- Units: Percentage increase in knowledge base utilization
- Example: 20% increase in knowledge base utilization
Employee satisfaction surveys: Gather feedback from employees on their perceived productivity gains, time savings, and overall satisfaction with the AI assistant. Positive feedback can lead to increased retention, better performance, and a more positive work environment.
-
- Units: Employee satisfaction score or percentage of employees reporting positive impact
- Example: 80% of employees report increased productivity and satisfaction with the AI assistant
It’s important to establish baseline measurements before introducing the AI assistant and then consistently track the relevant metrics over time. Additionally, conducting controlled experiments or pilot programs can help isolate the impact of the AI assistant from other factors affecting productivity.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we explored how you can use Amazon Q Business to build generative AI assistants that enhance employee experience and boost productivity. By seamlessly integrating with internal data sources, knowledge bases, and productivity tools, Amazon Q Business equips your workforce with instant access to information, automated tasks, and personalized support. Using its robust capabilities, including multi-source connectors, document enrichment, relevance tuning, and enterprise-grade security, you can create tailored AI solutions that streamline workflows, optimize processes, and drive tangible gains in areas like task completion times, issue resolution, onboarding efficiency, and cost savings.
Unlock the transformative potential of Amazon Q Business and future-proof your organization—contact your AWS account team today.
Read more about Amazon Q
About the Authors
 Puneeth Ranjan Komaragiri is a Principal Technical Account Manager at Amazon Web Services (AWS). He is particularly passionate about Monitoring and Observability, Cloud Financial Management, and Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen-AI) domains. In his current role, Puneeth enjoys collaborating closely with customers, leveraging his expertise to help them design and architect their cloud workloads for optimal scale and resilience.
Puneeth Ranjan Komaragiri is a Principal Technical Account Manager at Amazon Web Services (AWS). He is particularly passionate about Monitoring and Observability, Cloud Financial Management, and Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen-AI) domains. In his current role, Puneeth enjoys collaborating closely with customers, leveraging his expertise to help them design and architect their cloud workloads for optimal scale and resilience.
 Krishna Pramod is a Senior Solutions Architect at AWS. He works as a trusted advisor for customers, helping customers innovate and build well-architected applications in AWS cloud. Outside of work, Krishna enjoys reading, music and traveling.
Krishna Pramod is a Senior Solutions Architect at AWS. He works as a trusted advisor for customers, helping customers innovate and build well-architected applications in AWS cloud. Outside of work, Krishna enjoys reading, music and traveling.
 Tim McLaughlin is a Senior Product Manager for Amazon Q Business at Amazon Web Services (AWS). He is passionate about helping customers adopt generative AI services to meet evolving business challenges. Outside of work, Tim enjoys spending time with his family, hiking, and watching sports.
Tim McLaughlin is a Senior Product Manager for Amazon Q Business at Amazon Web Services (AWS). He is passionate about helping customers adopt generative AI services to meet evolving business challenges. Outside of work, Tim enjoys spending time with his family, hiking, and watching sports.
Source link
lol