This is T-Minus, where we count down the biggest developments in space, from new rocket launches to discoveries that advance our understanding of the universe and our place in it. Humanity is reaching new heights in space exploration. Make sure you’re part of the journey by subscribing above.
Space stations of the future
For more than 20 years, the International Space Station (ISS) has served as one of humanity’s few off-world homes, giving us a way to conduct groundbreaking research that wouldn’t have been possible on Earth’s surface.
Today, China also has a crewed space station, and ten new stations are now in the works. In no particular order, here are the space stations that will ensure humans can continue to take advantage of the space environment long after the ISS is finally deorbited in 2030.
Lunar Gateway
A concept image of the Lunar Gateway.
- Team leader: NASA (US / public)
- Location: Lunar orbit
- Deployment target: 2025 (but likely 2027)
- Capacity: 4 people
Claim to fame: The first lunar space station (maybe)
Quick recap: NASA plans to return astronauts to the moon’s surface with its upcoming Artemis missions and eventually send people to Mars. To support those astronauts and their research, it plans to build a space station in the moon’s orbit, with its partners at ESA, JAXA, and CSA.
What they’re saying: “We’ll need a place to orbit around the moon where we can live and work. A place to get ready for our lunar surface expeditions, and a place to return to when our work on the lunar surface is complete. We need a lunar home away from home. This will be the Gateway.” – Randy Bresnik, NASA astronaut
Haven-1
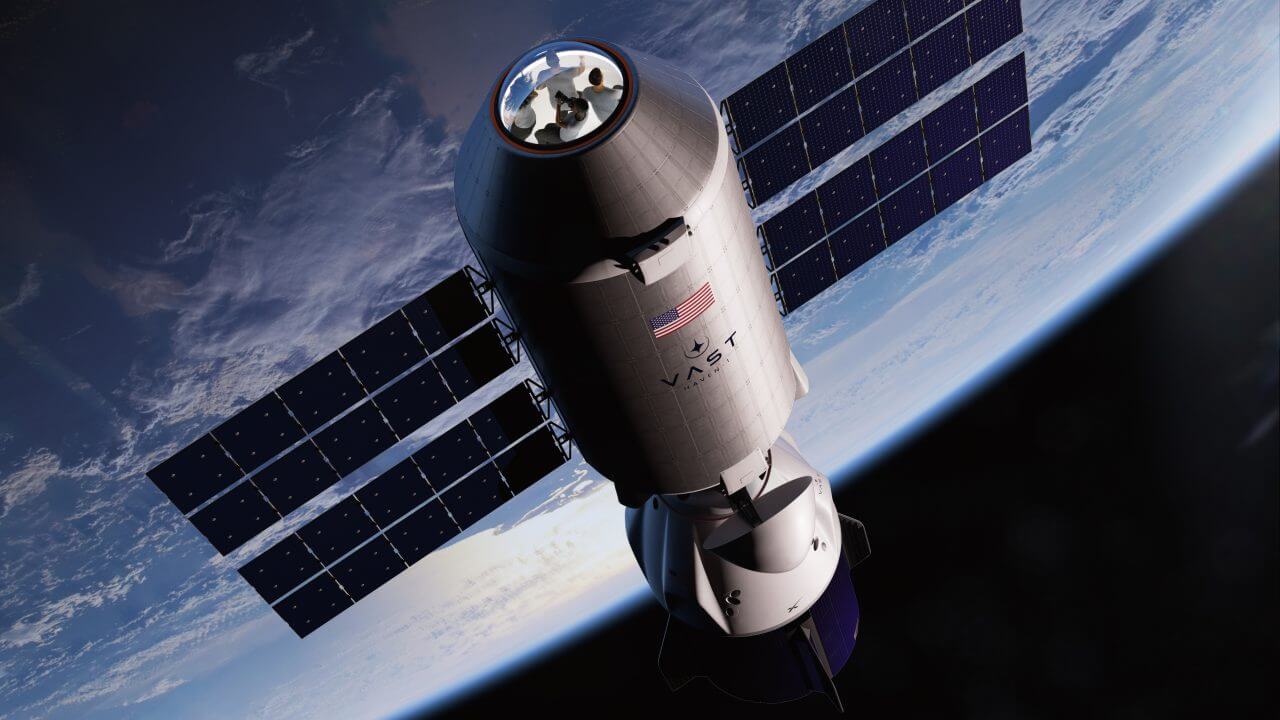

A concept image of Haven-1.
- Project lead: Vast (US / private)
- Location: Low-Earth orbit
- Deployment target: August 2025
- Capacity: 4 people
Claim to fame: The first commercial space station (maybe)
Quick recap: Vast’s plan is to have Haven-1 operate as an independent commercial space station when it is first launched but later connect it as a module on a bigger space station that it is currently developing. The company has already tapped SpaceX to launch Haven-1, as well as deliver its first crew of four astronauts.
What they’re saying: “A commercial rocket launching a commercial spacecraft with commercial astronauts to a commercial space station is the future of low-Earth orbit, and with Vast we’re taking another step toward making that future a reality.” – Tom Ochinero, senior VP of commercial business at SpaceX
Axiom Station
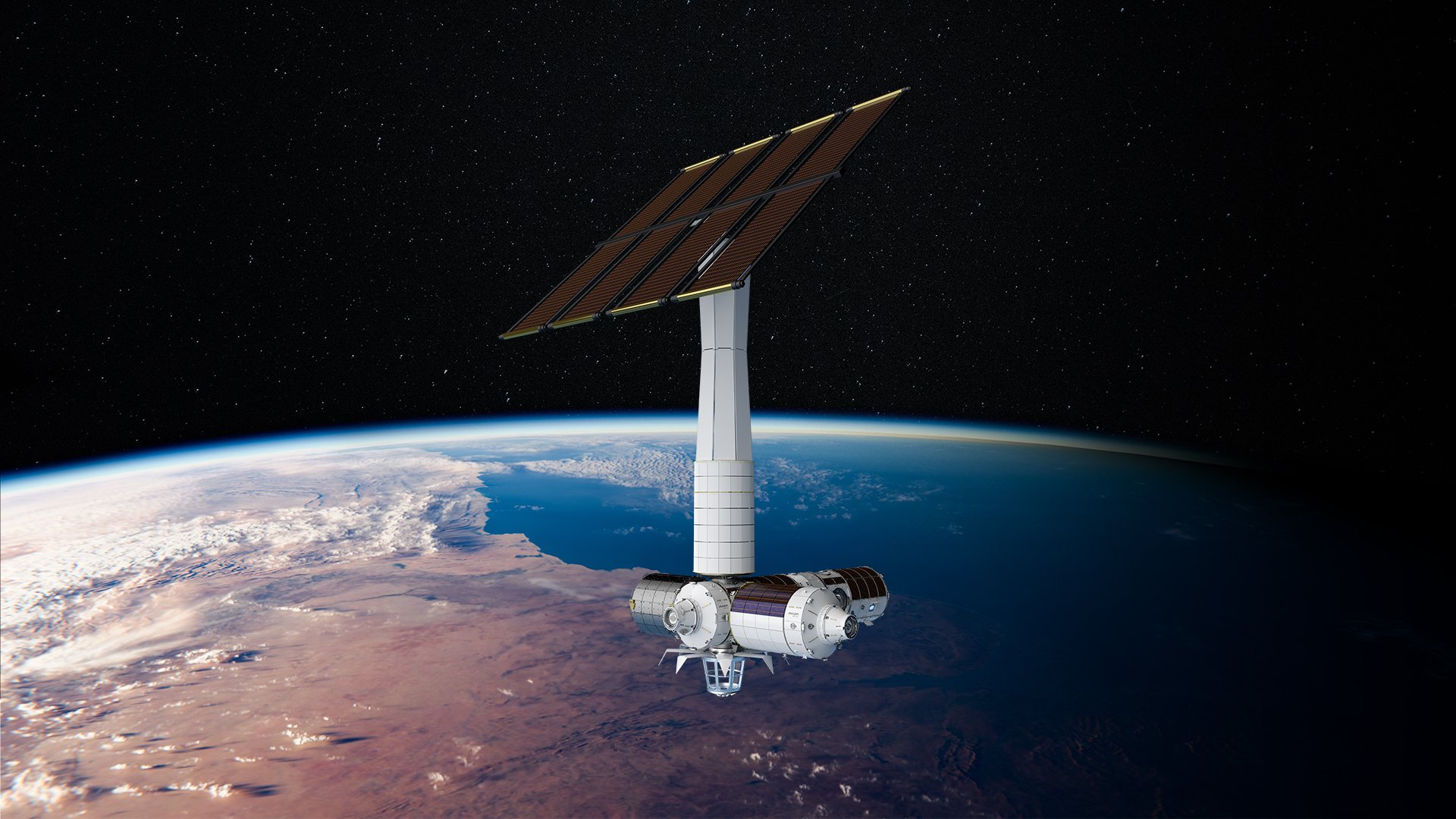

- Project lead: Axiom Space (US / private)
- Location: Low-Earth orbit
- Deployment target: 2026
- Capacity: 8 people
Claim to fame: NASA’s transition phase
Quick recap: In 2020, NASA awarded Axiom Space a contract to build and deploy at least one new space station module, attached to the ISS. When the ISS retires, the plan is to detach the Axiom module(s), allowing them to operate as an independent space station that NASA and other customers will be able to use for a fee.
What they’re saying: “Through our station, we will open up low-earth orbit to the world — to explore, to travel, to complete science in space and beyond.” – Mark Greely, executive VP of station program management at Axiom Space
Gravitics / Space Force collaboration
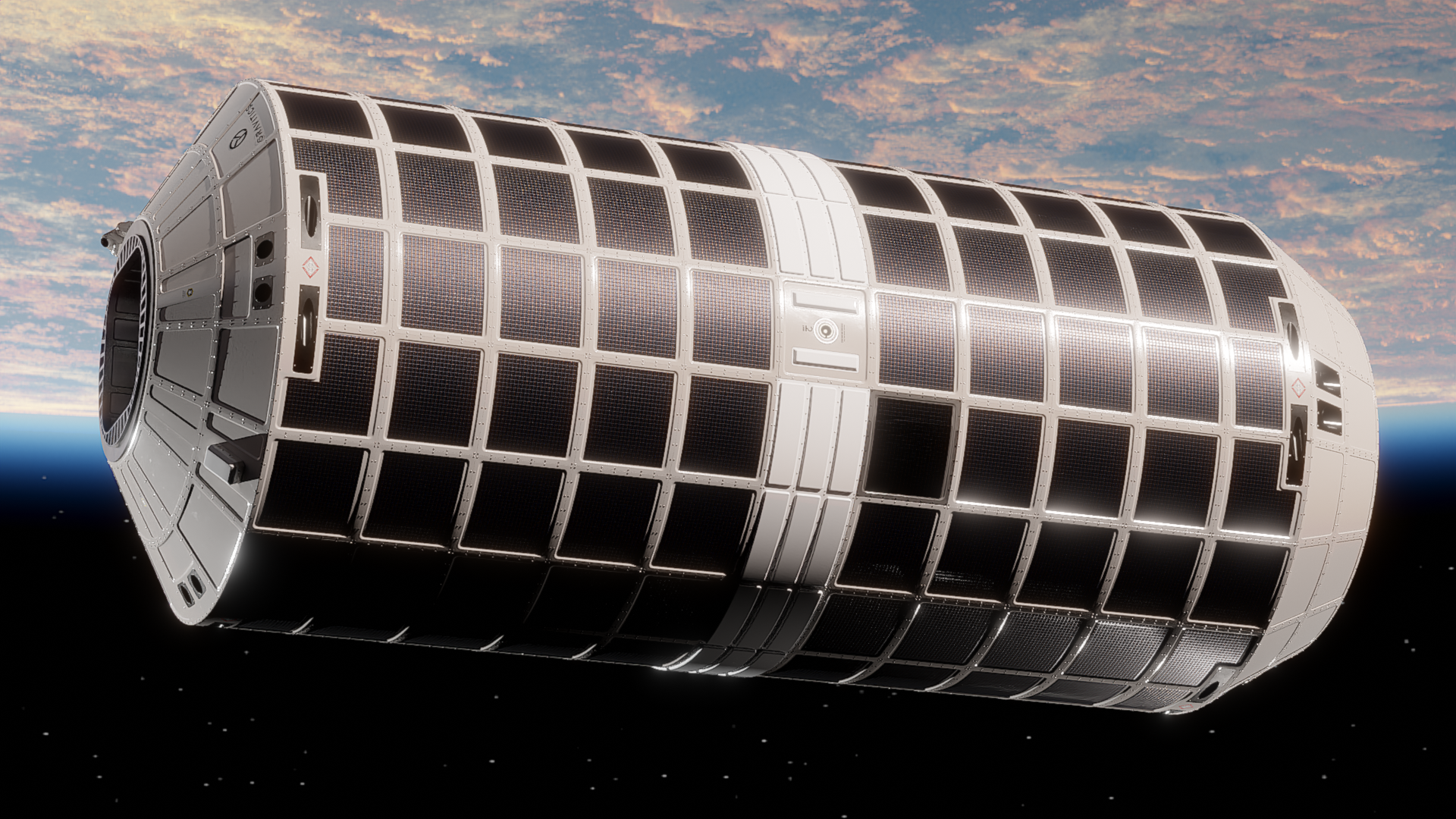
A concept image of a StarMax module.
- Project lead: Gravitics (US / private)
- Location: TBA
- Deployment target: TBA
- Capacity: TBA
Claim to fame: The Space Force’s space station
Quick recap: In April, the US Space Force awarded Gravitics a $1.7 million contract to develop orbital platforms as part of its tactically responsive space (TacRS) effort, which focuses on developing systems that will allow it to quickly and flexibly respond to threats in space. Details on how those platforms might differ from the company’s StarMax module or when they might be deployed have not been revealed.
What they’re saying: “The Gravitics space station module offers an unconventional and potentially game-changing solution for TacRS. As we look into the future, the innovative use of commercial technologies will be an important aspect to solving some of our toughest challenges.” – Jason Altenhofen, director of operations at the Space Force’s Space Safari Program Office
Russian Orbital Station
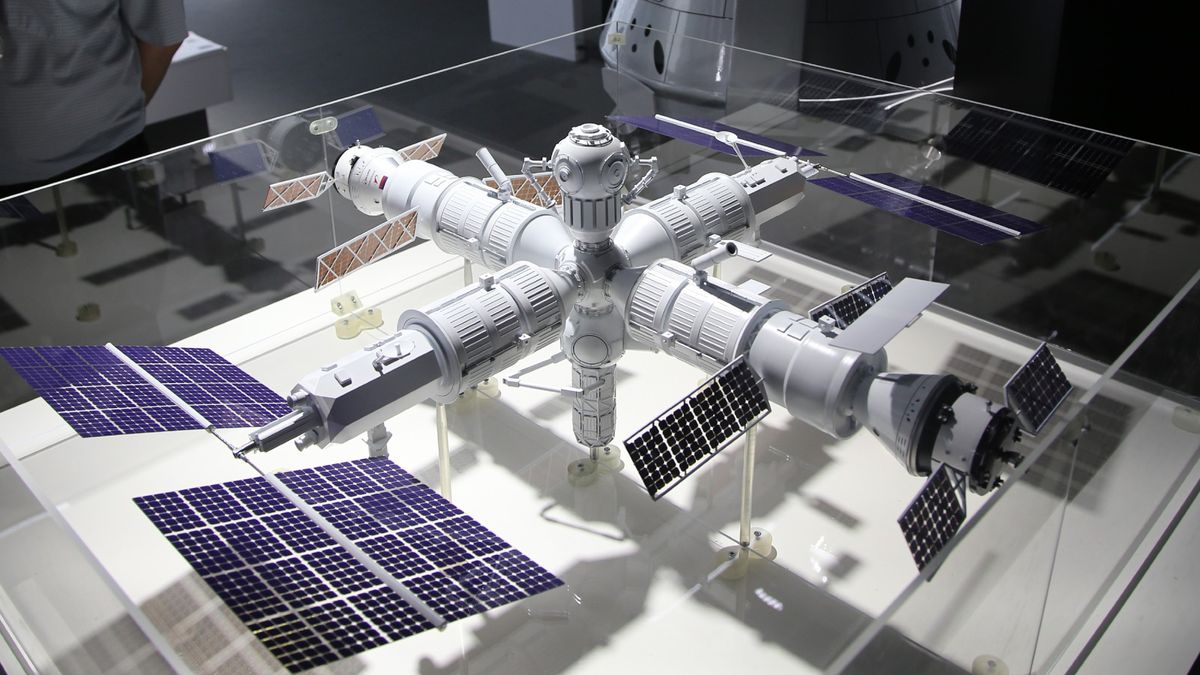

A model of Russia’s in-development space station.
- Project lead: Roscosmos (Russia / public)
- Location: Low-Earth orbit
- Deployment target: 2027
- Capacity: At least 2 people
Claim to fame: Russia’s ISS replacement
Quick recap: In 2022, Russia revealed plans to pull out of the ISS and build its own space station in Earth’s orbit. In July 2024, it announced a timeline for construction that will see an initial module deployed in 2027, with five more modules to follow before 2033. The plan is for the station to be able to operate autonomously or with a crew on board.
What they’re saying: “The station will have a high power supply capacity, which will make it possible to organize various experiments, test new technologies, develop new materials and medications, and will operate as a permanently functioning laboratory for testing space technologies.” – Yury Borisov, Roscosmos General Director
Orbital Reef
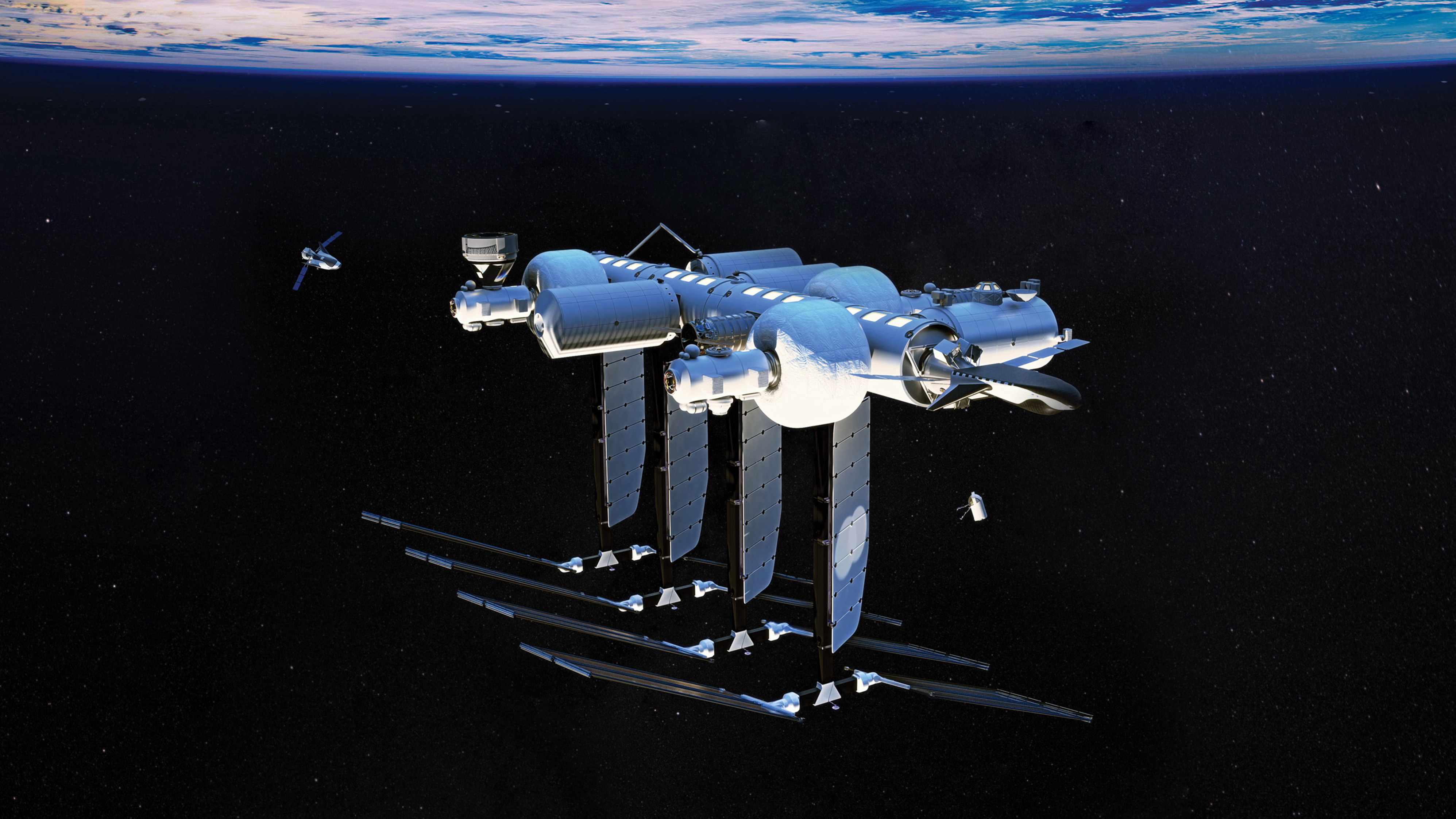
A concept image of Orbital Reef.
- Project leads: Blue Origin (US / private) and Sierra Space (US / private)
- Location: Low-Earth orbit
- Deployment target: 2027
- Capacity: 10 people
Claim to fame: The inflatable space station
Quick recap: In 2021, NASA awarded Blue Origin and Sierra Space a grant to develop Orbital Reef, another commercial space station NASA hopes to use after the ISS is retired. The station is made of a fabric that can be folded during launch and then inflated once in space — this allows it to be deployed in a single launch, which can cut down on costs.
What they’re saying: “Our revolutionary, expandable space station technology reinvents the space station. Our technology, for the first time, will enable the right unit economics that will usher in the full commercialization of space.” – Tom Vice, CEO of Sierra Space
LIFE Pathfinder
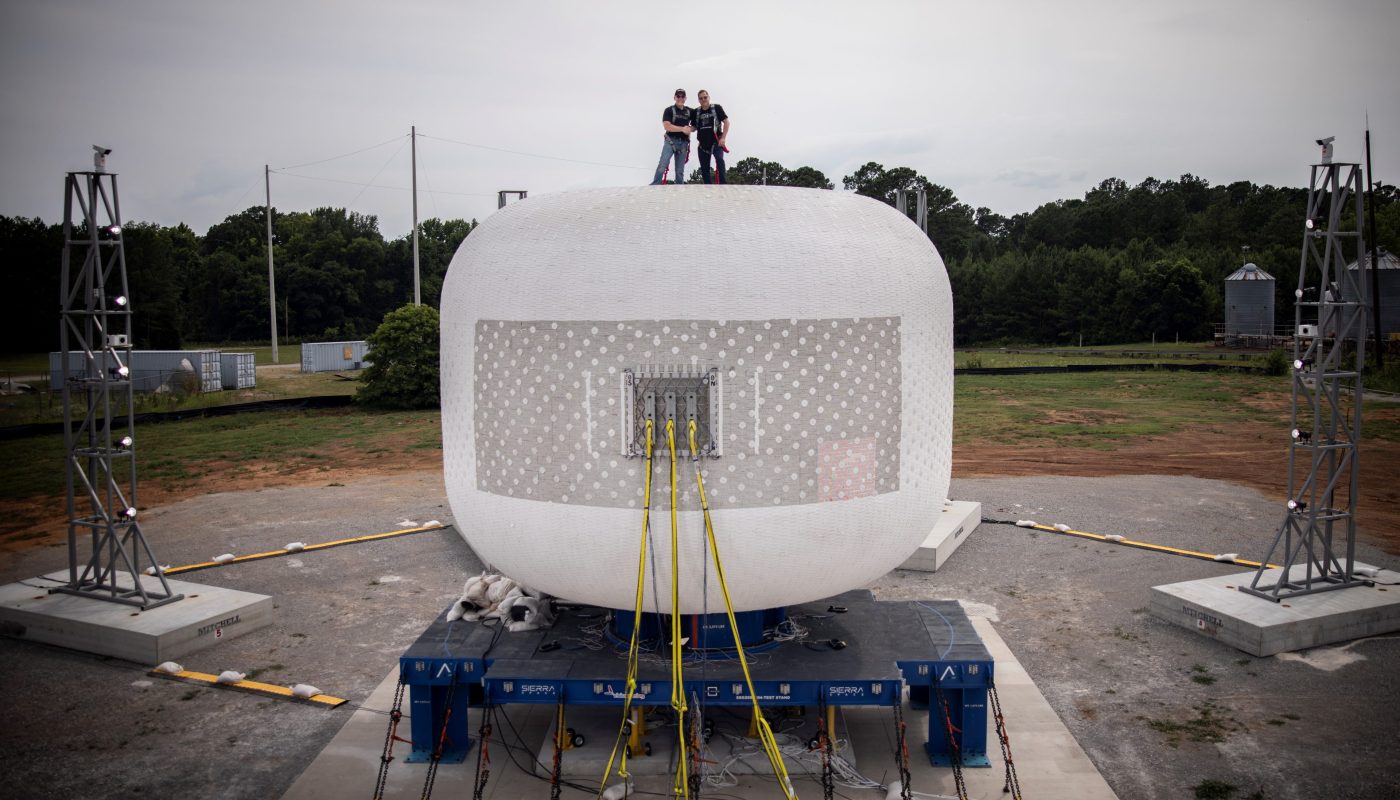

An inflated Orbital Reef module.
- Project lead: Sierra Space (US / private)
- Location: Low-Earth orbit
- Deployment target: 2026
- Capacity: 4 people
Claim to fame: The pilot
Quick recap: Before launching Orbital Reef with Blue Origin, Sierra Space plans to deploy a version of its inflatable module, known as the “Large Integrated Flexible Environment” (LIFE), as a stand-alone space station that could be used by commercial companies for biotech research.
What they’re saying: “Sierra Space’s inflatable space station technology offers the absolute largest in-space pressured volume, the best unit economics per on-orbit volume and lowest launch and total operating costs.” – Tom Vice, CEO of Sierra Space
Bharatiya Antariksh Station
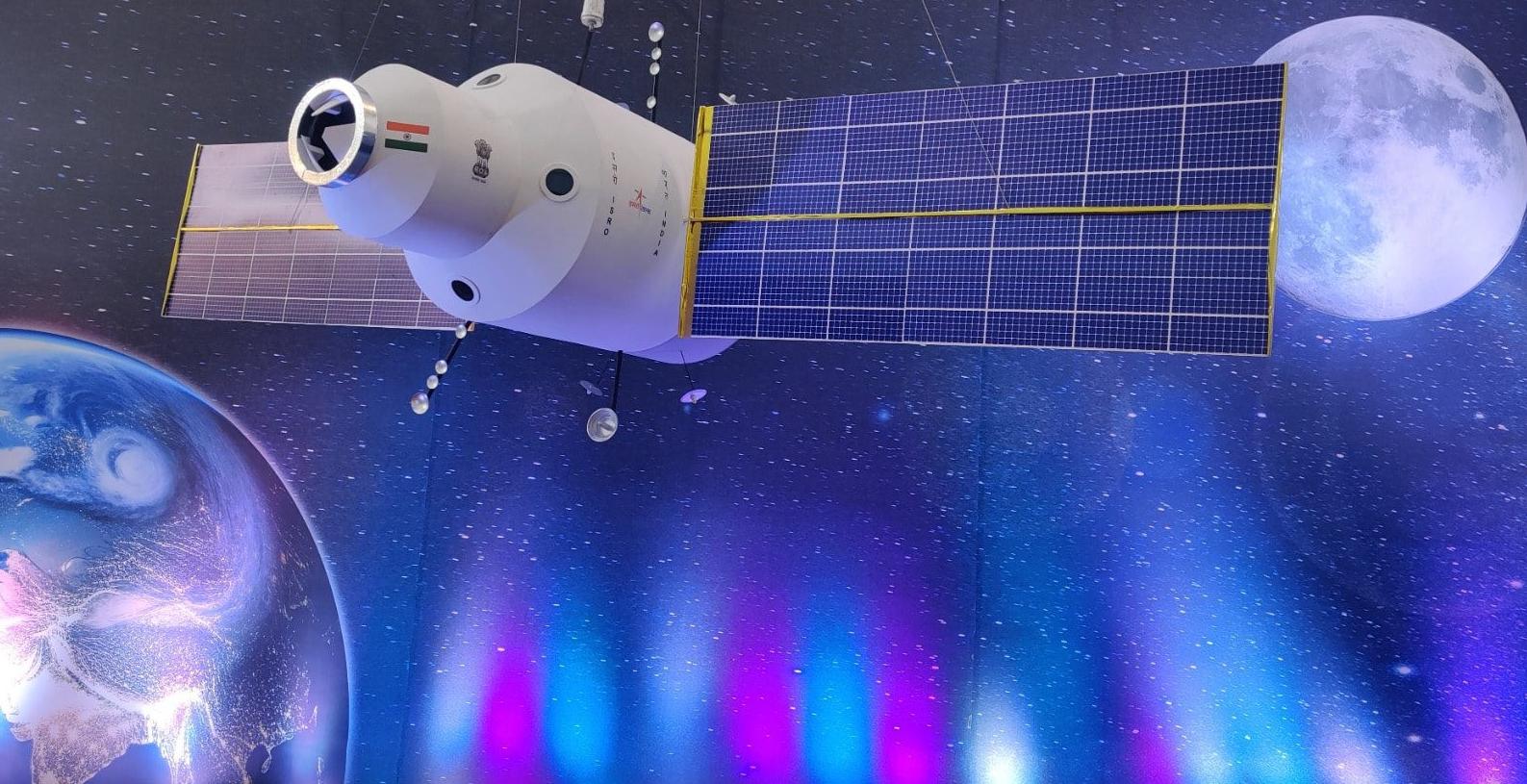

A concept image of ISRO’s in-development space station.
- The team: ISRO (India / public)
- Location: Low-Earth orbit
- Deployment target: 2028
- Capacity: 2-4 people
Claim to fame: India’s first space station
Quick recap: India’s space program is on the rise, having landed on the moon for the first time in 2023. That same year, ISRO’s chairman Sreedhara Panicker Somanath said the agency planned to launch the first module of an Indian space station in 2028, with construction wrapping by 2035.
What they’re saying: “India’s strides in the space sector over the past few years have been commendable and we are building on them for more successes. This includes the setting up of ‘Bharatiya Antariksha Station’ by 2035 and sending [the] first Indian to the moon by 2040.” – Narendra Modi, prime minister of India
Starlab
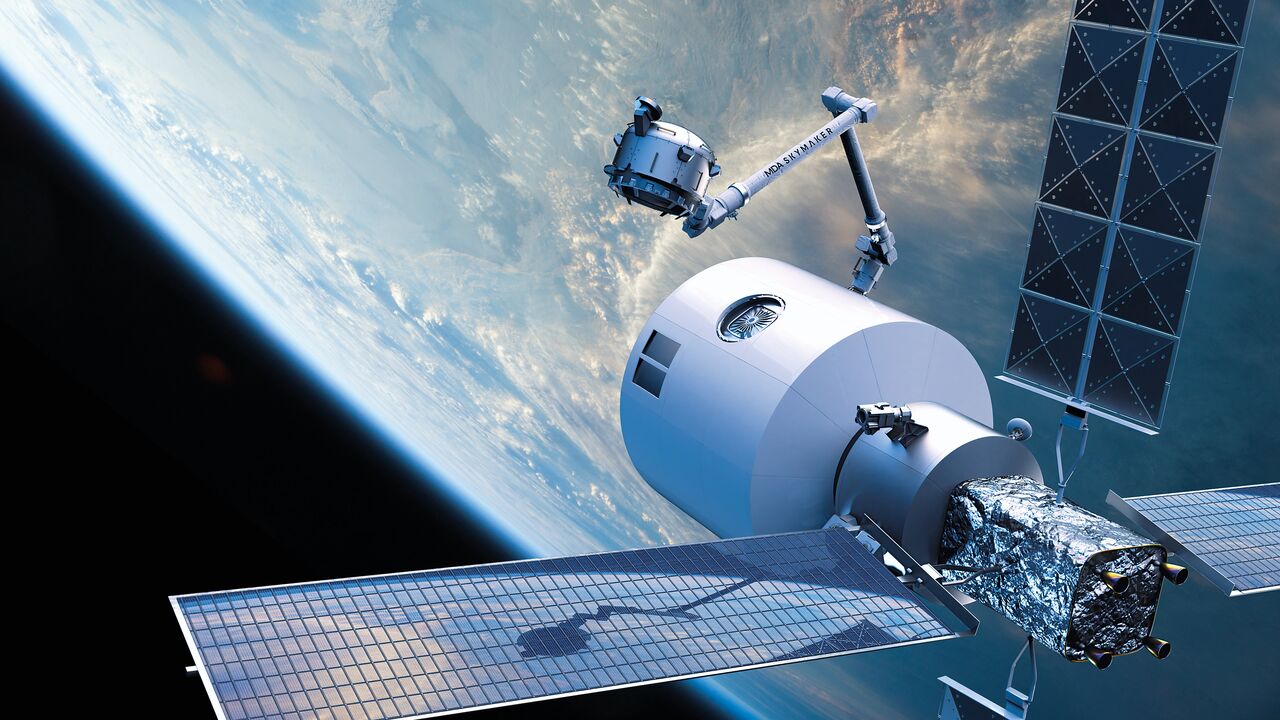

A concept image of Starlab.
- Project leads: Voyager Space (US / private) and Airbus (Europe / private)
- Location: Low-Earth orbit
- Deployment target: Before 2030
- Capacity: 4 people
Claim to fame: An international affair, with partners from every region involved in the ISS except Russia
Quick recap: Voyager Space subsidiary Nanoracks received a NASA grant to develop its space station, Starlab, in 2021. Since then, Airbus, Mitsubishi Corporation, MDA Space, and Palintir have joined the project.
What they’re saying: “We’ve been very focused from the beginning on this strategy to recreate the ISS except, instead of being owned by the government, it’s owned by the leading aerospace and defense corporations within those regions.” – Matthew Kuta, president of Voyager Space
The International Lunar Research Station (ILRS)
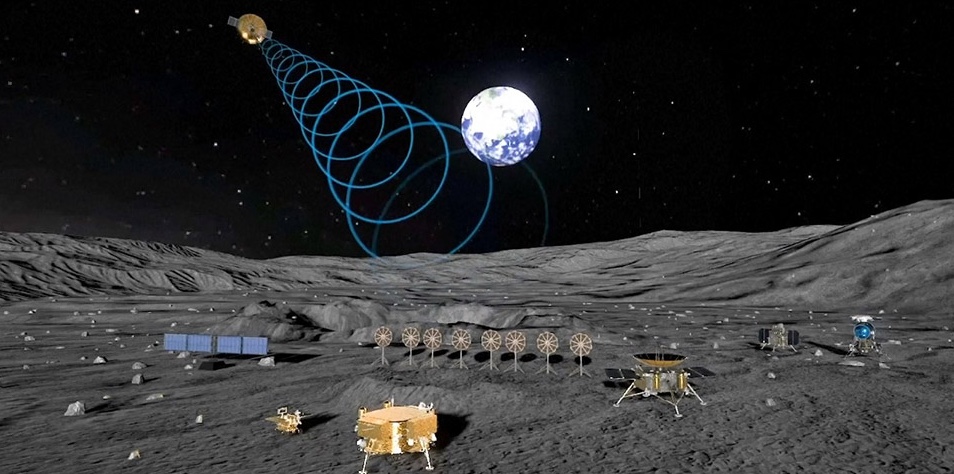

A concept image of the International Lunar Research Station.
- Project leads: Roscosmos (Russia / public) and CNSA (China / public)
- Location: Lunar orbit
- Deployment target: Completed by 2045
- Capacity: TBA
Claim to fame: The space station / moon base combo
Quick recap: In 2021, Russia and China announced plans to collaborate on a lunar base located either on the moon’s surface or in its orbit, but as of 2024, the plan seems to be to utilize both locations. The project has also expanded to include 12 more countries, including the United Arab Emirates, South Africa, and Pakistan.
What they’re saying: “The moon serves as a starting point, and an international lunar research station will provide a platform for long-term scientific research, work and habitation, paving the way for future human exploration into deeper space.” – Wu Weiren, chief designer of China’s lunar exploration program
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].
Source link
lol

