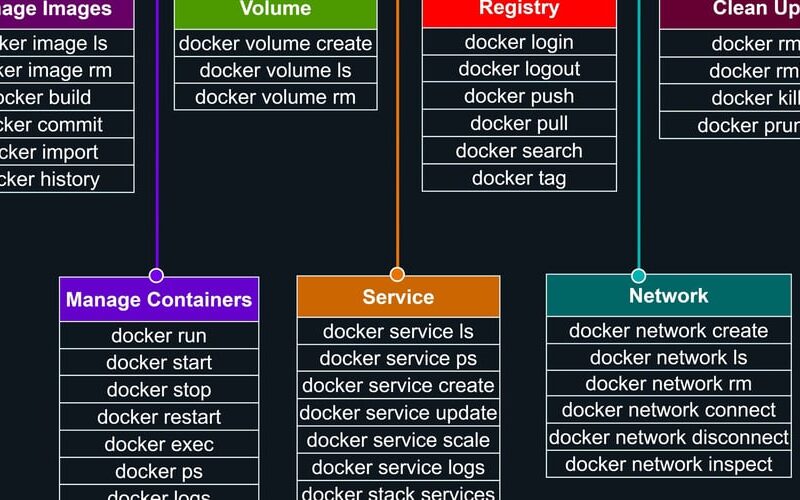
Here are some common Docker commands for managing containers, images, networks, and volumes:
1. Docker Container Commands:
-
Run a container:
docker run -d --name <container-name> <image-name>- Runs a container in detached mode (
-d) from the specified image. - Example:
docker run -d --name my-nginx nginx
- Runs a container in detached mode (
-
List running containers:
docker ps- Shows all currently running containers.
- Add
-ato list all containers, including stopped ones.
-
Stop a container:
docker stop <container-id|container-name>- Stops a running container.
-
Remove a container:
docker rm <container-id|container-name>- Deletes a stopped container.
- Use
-fto force-remove a running container.
2. Docker Image Commands:
-
Build an image:
docker build -t <image-name>:<tag> <path-to-dockerfile>- Builds an image from a Dockerfile.
- Example:
docker build -t my-app:latest .
-
List images:
docker images- Lists all images available on the host.
-
Remove an image:
docker rmi <image-id|image-name>- Deletes an image.
- Use
-fto force-remove an image if it’s being used.
-
Pull an image from a repository:
docker pull <image-name>:<tag>- Downloads an image from Docker Hub or other registries.
- Example:
docker pull ubuntu:latest
3. Docker Network Commands:
-
List networks:
docker network ls- Shows all Docker networks.
-
Create a network:
docker network create <network-name>- Creates a new Docker network.
-
Connect a container to a network:
docker network connect <network-name> <container-name> -
Inspect a network:
docker network inspect <network-name>- Shows detailed information about a Docker network.
4. Docker Volume Commands:
-
Create a volume:
docker volume create <volume-name>- Creates a new volume for persistent storage.
-
List volumes:
docker volume ls- Lists all Docker volumes.
-
Remove a volume:
docker volume rm <volume-name> -
Inspect a volume:
docker volume inspect <volume-name>- Shows detailed information about a volume.
5. Miscellaneous Commands:
-
View container logs:
docker logs <container-id|container-name>- Displays logs from a specific container.
- Use
-fto follow the logs in real-time.
-
Access a running container’s shell:
docker exec -it <container-id|container-name> /bin/bash- Starts an interactive shell inside a running container.
- Example:
docker exec -it my-nginx /bin/bash
-
Tag an image:
docker tag <image-name> <repository>/<image-name>:<tag>- Tags an image to prepare it for pushing to a registry.
- Example:
docker tag my-app myrepo/my-app:latest
-
Push an image to a registry:
docker push <repository>/<image-name>:<tag>- Uploads an image to a Docker registry.
-
Prune unused containers, images, networks, and volumes:
docker system prune- Cleans up unused resources.
- Add
-ato remove all stopped containers and unused images.
These commands cover most of the typical operations when working with Docker, such as managing containers, images, and networking.
Source link
lol